Dark Launches
Dark Launches are a method of deploying new features into production while keeping them hidden from most users until the official release. The main goal is to deploy the functionality in a real-world environment to test its performance, stability, and integration with existing systems without impacting end users.
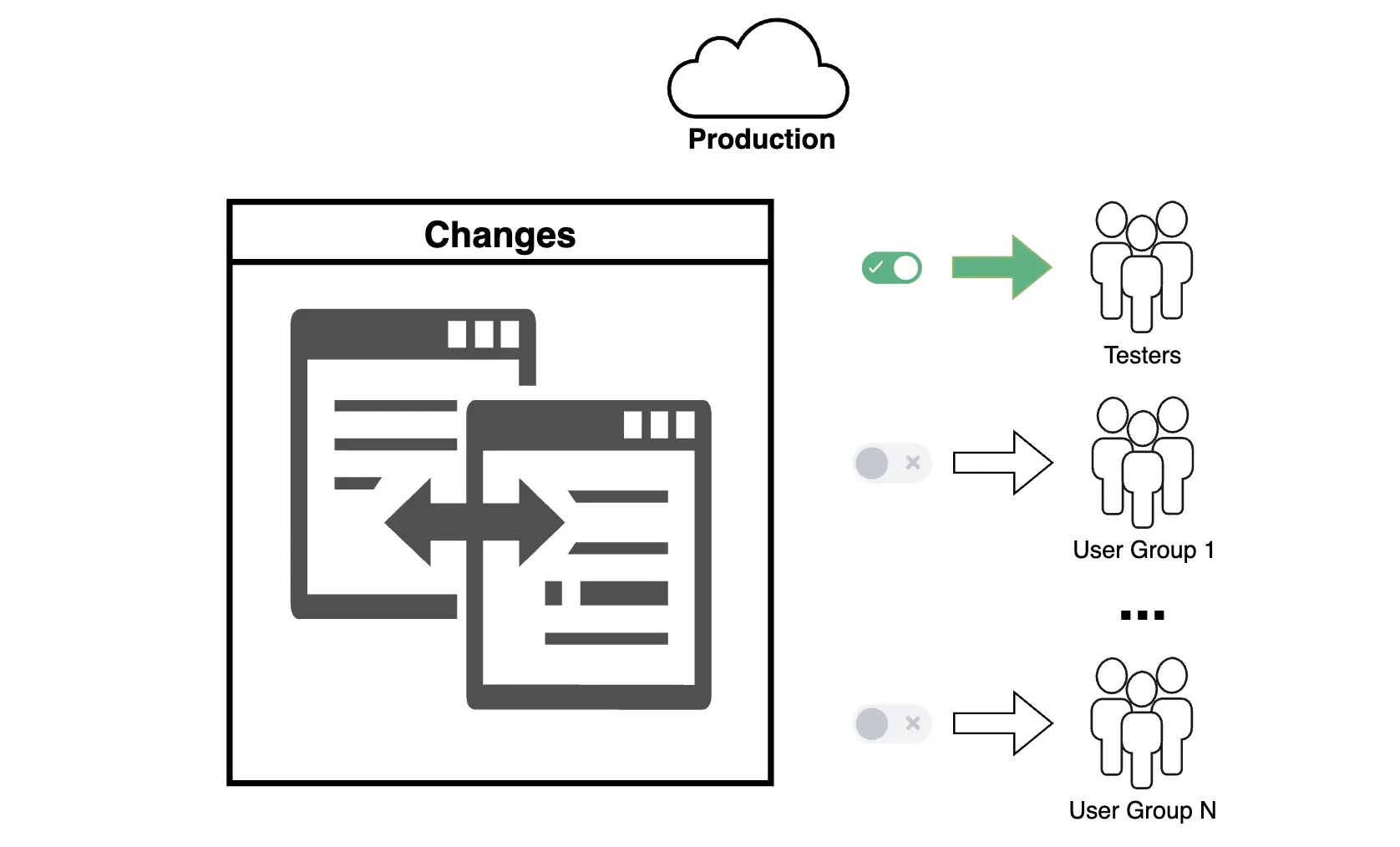
Dark Launches are widely used in modern change management approaches, such as DevOps and Continuous Delivery, to minimize risks associated with new releases.
For example, a new feature might be deployed to the production environment but only activated for a limited audience (e.g., internal testers or an admin group) until the team is confident in its readiness for a public launch.
Dark Launches are a powerful tool for improving release quality, especially in Salesforce projects with high loads, complex integrations, or strict stability requirements. When implemented correctly, this approach allows teams to minimize risks, collect key metrics, and successfully roll out changes while ensuring high quality.
Phased Rollouts vs. Dark Launches: Key Differences
While both approaches focus on risk management and incremental changes, their goals differ:
- Phased Rollouts aim to gradually increase the audience for a feature that is already production-ready.
- Dark Launches focus on testing hidden functionality in a production environment before its mass activation.
How Do Dark Launches Work?
Dark Launches rely on the following principles:
-
Decoupling Deployment and Activation
The new functionality is deployed in the environment, but its activation is controlled through access management mechanisms (e.g., Feature Flags). -
Incremental Testing
The feature is activated for a limited group of users (e.g., employees) or on specific data segments. -
Metric Collection and Feedback
Key performance indicators, such as performance, load, stability, and feedback from test users, are analyzed.
Implementing Dark Launches in Salesforce
Salesforce provides tools that enable effective implementation of Dark Launches. Key strategies include:
1. Feature Flags
Feature Flags allow functionality to be turned on or off without code changes or redeployment.
- Use Custom Metadata or Custom Settings to store feature flags.
- Configure logic in Apex or Flows to check flag status before activating functionality.
2. Custom Permissions and Permission Sets
- Restrict access to new features for specific user groups via Custom Permissions.
- Manage access with Permission Sets, enabling feature activation for test groups.
3. Validation Rules and Record Types
- Configure Validation Rules to restrict access to new functionality at the data level.
- Use Record Types to manage visibility of new records or fields.
4. User Segmentation
- Divide users into groups, such as Public Groups or Roles, to fine-tune access to features or data.
5. UI-Level Control
- Hide new components or pages in Lightning using Component Visibility.
- Use Apex or LWC to apply conditions for feature visibility in the user interface.
6. Monitoring and Analysis
- Log feature usage through Apex Debug Logs or custom reports.
- Set up monitoring via Event Monitoring to analyze user interactions with the feature.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dark Launches
Advantages
-
Risk Minimization
Issues can be identified and resolved before the functionality is available to all users, reducing error likelihood. -
Real-World Testing
The feature is tested in a live environment, uncovering problems not found in isolated tests. -
Smooth Transition
A gradual rollout ensures a seamless activation for all users after successful testing. -
A/B Testing Support
Dark Launches can be used to test multiple variants of a feature before its final activation.
Disadvantages
-
Increased Development Complexity
Implementing Feature Flags and managing hidden functionality requires additional effort. -
Risk of Prolonged Use
Keeping functionality hidden for too long can lead to code complexity and maintenance challenges. -
Need for Clear Management
Monitoring systems and processes are required to remove outdated Feature Flags and control feature activity.
Use Cases for Effective Dark Launches
Dark Launches are especially useful in the following scenarios:
1. Performance Testing
When testing how new functionality will perform in a real-world production environment, Dark Launches allow teams to:
- Assess the feature’s impact on system performance.
- Identify bottlenecks or scalability issues.
- Optimize the system before a mass launch.
2. Compatibility Testing
In complex projects with integrations or large datasets, Dark Launches ensure:
- The new feature does not conflict with existing processes or systems.
- Risks to integrations and user data are minimized.
3. Gathering Feedback from Key Users
Dark Launches provide early access to:
- Internal testers.
- Business representatives and key users, allowing for valuable feedback.
- This helps address potential issues and incorporate user requests.
4. Preparation for A/B Testing
A/B Tests For launching multiple feature variants, Dark Launches:
- Enable testing in a live environment.
- Help choose the optimal variant based on data and user experience.
5. Complex or Critical Releases
For changes with significant business impact, Dark Launches:
- Ensure stability and security before a large-scale launch.
- Minimize risks of failures and negative user impact.
6. Multi-Region or Multi-Product Projects
In organizations with multiple production environments, Dark Launches:
- Allow functionality testing in each environment step by step.
- Ensure process consistency and reduce global failure risks.
7. High-Load Features
For new features involving significant workloads (e.g., mass requests or data processing), Dark Launches:
- Test the feature under real-world load conditions.
- Identify and resolve potential issues before escalation.